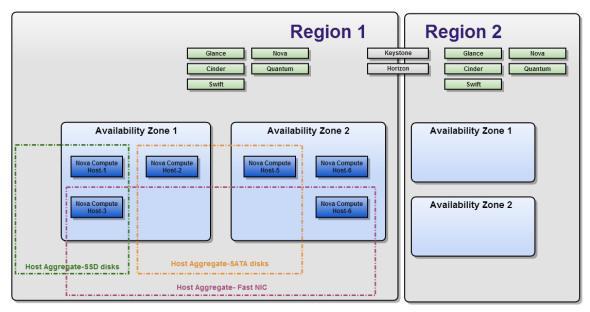
OpenStack was made from the ground up to scale to thousands of nodes and span different datacenters and geographical regions. For this reason, Openstack clouds can be divided in three main hierarchical zones: Regions, Availability Zones and Host Aggregates.
Region
Each Region has its own full Openstack deployment, including its own API endpoints, networks and compute resources. Different Regions share one set of Keystone and Horizon services, to provide access control and a Web interface.
Availability Zone
Inside a Region, compute nodes can be logically grouped into Availability Zones (AZ): when launching a new VM instance we can specify the AZ we want it instantiated in, or even a specific node inside an AZ to run the VM instance.
Host Aggregates
Besides AZs, compute nodes can also be logically grouped into Host Aggregates.
Host Aggregates have meta-data to tag groups of compute nodes, e.g. all nodes with an SSD disk can belong to one Host Aggregate, while another Host Aggregate may contain all nodes with 10 GB NICs.
One compute node can be put into both an Host Aggregate and an Availability Zone at the same time, as they do not conflict. Moreover, one compute node can belong to more than one Host Aggregate. Host Aggregates are visible only to the admin and can also be used to mix hypervisors in the same AZ, for example to save license costs: some vendors provide free guests for their hypervisors.
Cells
OpenStack Compute cells allow you to run the cloud in a distributed fashion. Hosts in a cloud are partitioned into groups called cells. Cells are configured in a tree. The top-level cell ("API cell") has a host that runs the nova-api service, but no nova-compute services.
This allows for a single API server being used to control access to multiple cloud installations. Introducing a second level of scheduling (the cell selection), in addition to the regular nova-scheduler selection of hosts, provides greater flexibility to control where virtual machines are run.
Unlike having a single API endpoint, regions have a separate API endpoint per installation, allowing for a more discrete separation. Users wanting to run instances across sites have to explicitly select a region. However, the additional complexity of running a new service is not required.