- Details
-
Category: Word of the Day
-
Published: Thursday, 26 January 2017 17:34
-
Written by Guru Advisor
XML stands for eXtensible Markup Language and defines a markup language that is based on a specific syntax to define and control the meaning of the elements contained in a text. The main characteristic of XML is creating custom tag, hence the name eXtensible.
XML is also often used to export data in a standard format from a proprietary database.
- Details
-
Category: Word of the Day
-
Published: Tuesday, 24 January 2017 17:34
-
Written by Guru Advisor
The term Ads (Advertising) is a generic term for all advertising communication techniques that are used to promote a certain product. In the IT world it’s commonly found while browsing the Web as banners inside Web pages that capture the attention of the reader.
You can limit or block Ads while browsing by installing an “Ad-blocker”.
- Details
-
Category: Word of the Day
-
Published: Tuesday, 24 January 2017 17:34
-
Written by Guru Advisor
The term Ad-blocker defines a browser component (if talking about Web browsing) which can intercept and block ads within a Web page that can be annoying, hinder the experience and slow the loading because of all those extra ads content.
- Details
-
Category: Word of the Day
-
Published: Monday, 23 January 2017 17:34
-
Written by Guru Advisor
Crontab is a UNIX command that creates a table (or list) of commands that the operating system will execute automatically according to a certain schedule. The crontab command creates a file called Crontab file.
- Details
-
Category: Word of the Day
-
Published: Friday, 20 January 2017 10:00
-
Written by Guru Advisor
The acronym ACL stands for Access Control List and basically defines a table used by an operating system, or a firmware (ie network devices) where access rights to resources are specified for each user. Every object in the system has a specific security attribute which identifies its own ACL and regulates the usage by part of users according to the assigned privileges.
- Details
-
Category: Word of the Day
-
Published: Thursday, 19 January 2017 10:00
-
Written by Guru Advisor
The term Domain Controller (DC) defines a specific role typical of the Windows Server operating system that is assigned to the host that will manage the authentication of users in a domain environment. A DC can be Primary (PDC) or Backup (BDC); the former periodically sends an up-to-date copy of the users database to BDCs (which can be more than one) in order to guarantee uptime if it fails.
- Details
-
Category: Word of the Day
-
Published: Wednesday, 18 January 2017 10:00
-
Written by Guru Advisor
FQDN is the acronym for Fully Qualified Domain Name, which is the part of the URL that univocally identifies the server it’s being contacted across the Internet. The FQDN includes the second-level domain and all related subdomains, which basically is anything is left of the TLD extension (xxxx.example.com, xxx2.example.com etc.).
- Details
-
Category: Word of the Day
-
Published: Tuesday, 17 January 2017 10:06
-
Written by Guru Advisor
The term crawler describes a type of software the visits Web sites available on the Internet and checks content and information with the aim of creating search engines indexes and keeping them up-to-date. One of the particular features of a crawler is being able to visit each single page of a Website by also following any additional external links present.
- Details
-
Category: Word of the Day
-
Published: Wednesday, 04 January 2017 10:00
-
Written by Guru Advisor
The term Custom TLD, or Custom Top Level Domain, indicates those domain names that have been introduced and recognized by the ICANN association since April 2012. The most known TLDs like the historical .com, .net. and .org are now sided by custom domains and from then it’s possible to buy and use extensions such as .car, .home, .hobby and even .organization_name.
- Details
-
Category: Word of the Day
-
Published: Tuesday, 03 January 2017 10:06
-
Written by Lorenzo Bedin
Eye-Fi is the name of a technology used with memory cards to transfer data from the card to the destination device in a wireless manner.
Usually memory cards with Eye-Fi capabilities are used with digital cameras.
- Details
-
Category: Word of the Day
-
Published: Monday, 02 January 2017 10:06
-
Written by Lorenzo Bedin
The term Dynamic DNS, or DDNS, describes a mechanism with which a DNS system is automatically updated as soon as the associated IP address (or domain) is changed.
A classic application of DDNS is when a host with a public IP must be in perfect correspondence with the same domain name.
In order to work, a DDNS requires a client to be installed on the host which owns the interested IP address or, as an alternative, it’s often integrated with the firmware of gateways and routers.
- Details
-
Category: Word of the Day
-
Published: Friday, 30 December 2016 10:06
-
Written by Lorenzo Bedin
The term public key infrastructure (PKI) usually describes the set of technologies that allow users on the Internet to establish secure connections to Web sites, services and other users. Such connections are secure thanks to the use of private and public encryption keys, which are provided by a dedicated authority called Certification Authority.
- Details
-
Category: Word of the Day
-
Published: Thursday, 29 December 2016 17:06
-
Written by Lorenzo Bedin
Bugzilla is an open source Web platform developed by the Mozilla Foundation that is used to track bugs in software. Within the Mozilla Foundation, Bugzilla is used to track bugs related to the project of the association itself, like Firefox and Thunderbird.
Any user can open a ticket with Bugzilla so that developers can start to work on it.
- Details
-
Category: Word of the Day
-
Published: Tuesday, 06 December 2016 08:30
-
Written by Guru Advisor
The term sniffer describes a software tool capable of intercepting (sniffing) data on a network, thus forcing a network card to accept packets that are not addresses to it. That allows the sniffer to grab all traffic without needing any authorization. For instance a password sniffer can analyze and record all the traffic on the network and collect all packets containing a password.
- Details
-
Category: Word of the Day
-
Published: Monday, 05 December 2016 08:30
-
Written by Guru Advisor
The term subnet mask indicates a 32-bit number that defines how many bits of the IP address of a host describe the network the host belongs to and how many the number of hosts belonging to the same network.
Usually it’s expressed in the form 255.255.255.0 or /24.
In general, 16 and 24-bit subnet masks are used, that is, the first N bits defines the network and the remaining describe single hosts.
- Details
-
Category: Word of the Day
-
Published: Monday, 05 December 2016 08:30
-
Written by Guru Advisor
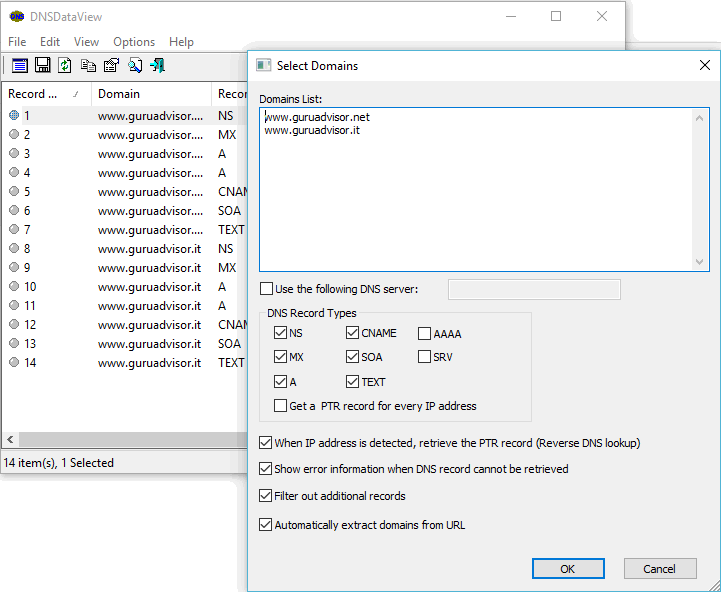
A DNS server (Domain Name System) is a server that manages, stores and computer Internet domain names with the related records. In other words, a DNS server translates IP addresses into domain names and vice-versa on an IP network. With DNS Lookup it’s usually intended that process that gives a DNS record from the server itself.
- Details
-
Category: Word of the Day
-
Published: Friday, 02 December 2016 08:30
-
Written by Guru Advisor
Subnetting is a strategy used to subdivide a single network into smaller logical subnetworks (subnets), thus reducing the net network traffic and hiding the overall structure of the network itself to clients. On a geographical standpoint, subnetting allows a company to add subnets without having to purchase additional networks from their own ISP.
Subnet masks, which are one of the configuration parameters of the TCP/IP protocol, determines which subnet a client belongs to.
- Details
-
Category: Word of the Day
-
Published: Friday, 02 December 2016 08:30
-
Written by Guru Advisor
The term downlink refers to the process of sending data through the network from an upper to a lower level; traditionally, it’s used in the context of satellite transmissions, but it cans also be used in an IT context with regards to the flow of data between computers through networks.
As for the upstream, the unit of measure is Kilobyte.
- Details
-
Category: Word of the Day
-
Published: Thursday, 01 December 2016 08:30
-
Written by Guru Advisor
A thin client is a computer connected to a network which locally has limited software and is highly dependant upon the resources available on the network. Historically, this concept is related to mainframes, when clients were only used to connect to the central computer, which had a very powerful hardware and only ran software used remotely.
- Details
-
Category: Word of the Day
-
Published: Wednesday, 30 November 2016 08:30
-
Written by Guru Advisor
Upstream is the term used to indicate the sending or the flux of data from a client towards a server or remote destination. The speed at which the data transmission happens is called upstream rate.